Media Fragmentation Analysis
Cross-platform information consumption patterns
This project investigates how audiences fragment across different media platforms and information sources in the modern media ecosystem. We develop methods to track and analyze cross-platform consumption patterns, revealing how people navigate between traditional broadcast media, cable news, and web-based information sources.
Key contributions include:
- Cross-platform measurement frameworks linking web and television consumption at the individual level
- Partisan news diet quantification measuring ideological segregation across different media types
- Supply and demand analysis separating audience preferences from platform availability
- Demographic fragmentation patterns identifying which groups rely on which information sources
- Temporal evolution tracking documenting how fragmentation changes over time and in response to major events
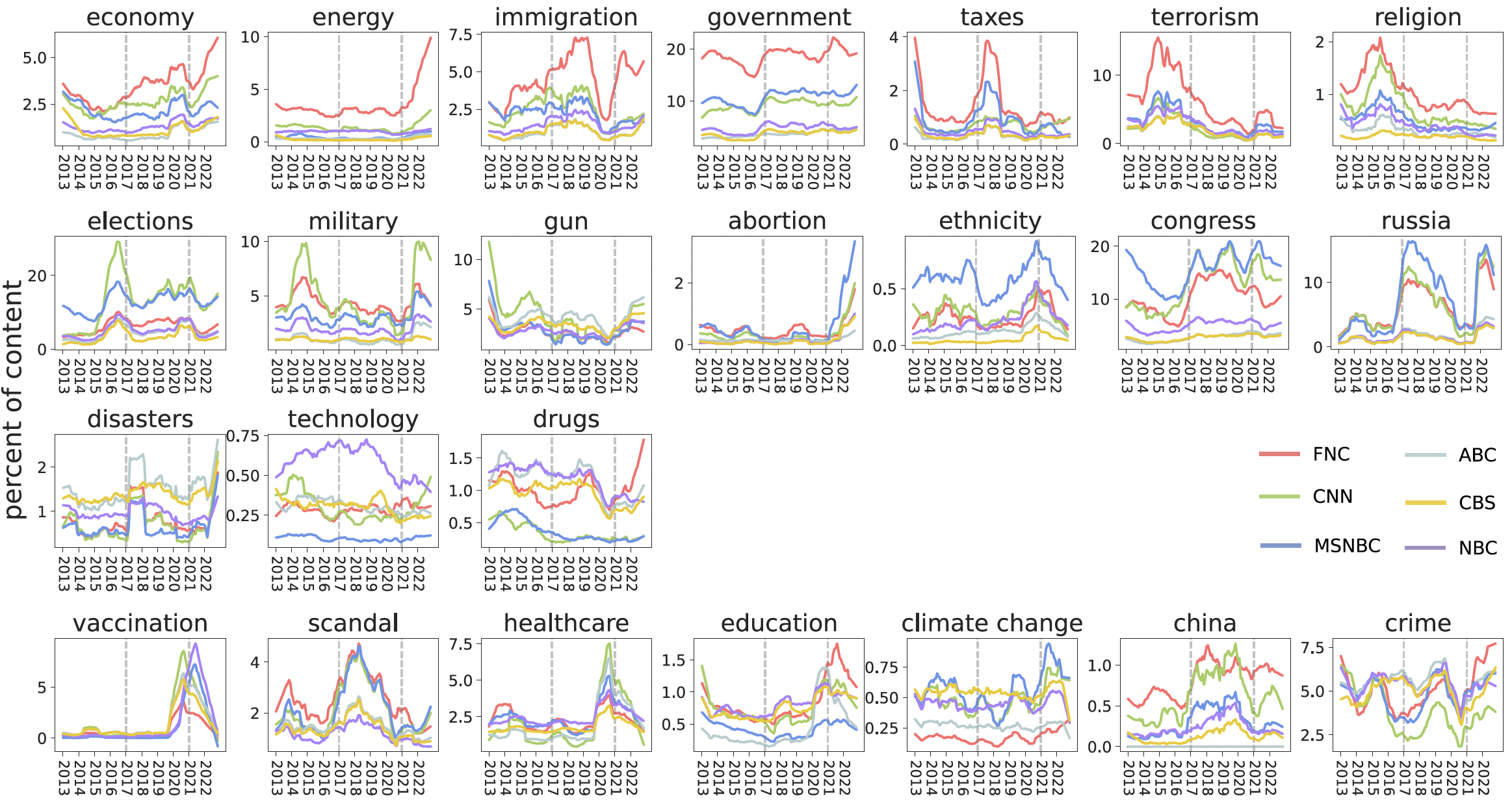
Our research reveals that while web-based news consumption is highly fragmented and ideologically segregated, television—particularly broadcast networks—continues to provide a relatively common information environment. However, this shared space is shrinking as audiences migrate away from traditional news consumption entirely.
Featured Research
Quantifying partisan news diets in Web and TV audiences Muise, D., Hosseinmardi, H., Howland, B., Mobius, M., Rothschild, D., & Watts, D. J. (2022). Science Advances, 8(28).
This study provides the first large-scale comparison of partisan news consumption across web and television platforms. Using comprehensive behavioral data from tens of thousands of U.S. participants, we quantify how news exposure differs between online and traditional media environments. We find that while online news diets are more fragmented and partisan-segregated, television—particularly broadcast networks—continues to provide a shared information commons. The research reveals fundamental differences in how platform architectures shape information exposure, with important implications for understanding political polarization and the erosion of shared reality in the digital age.